Languages
FAQs
Legal
- Guidance on sending the European Investigation Orders to and from the UK
- European Investigation Order: A judicial decision issued or validated by a judicial authority of a Member State ("the issuing State") in order to have one or several specific investigative measure(s) carried out in another Member State ("the executing State") with a view to obtaining evidence in criminal matters.
- New principle: same celerity and priority as for a similar domestic case.
- The EIO Directive sets the following time limits:
- 30 days for deciding on recognition or execution of an EIO (Art. 12(3));
- 90 days for carrying out investigative measures following the taking of the aforementioned decision (Art. 12(4));
- 24 hours, where practicable, for decision on provisional measure following the receipt of an EIO (Art. 32(2)).
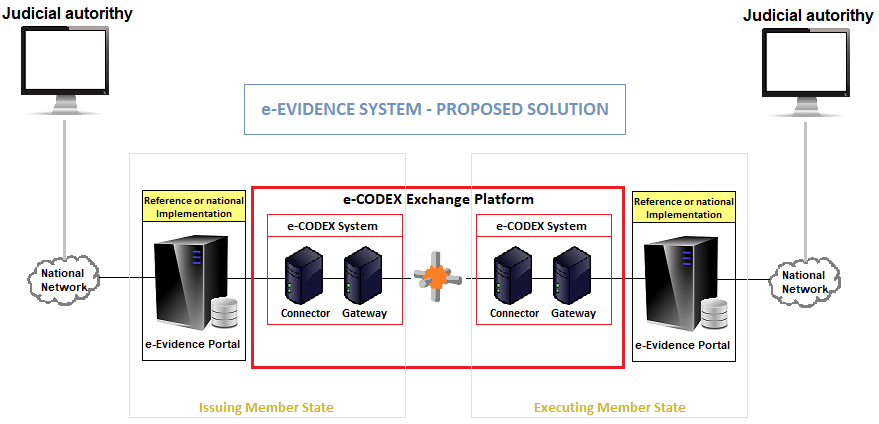
- Through the e-evidence portals, there will be one in each country. A platform with a secure communication channel for digital exchanges of EIOs for electronic evidence between EU judicial authorities.
Referred to the evidence project page http://www.evidenceproject.eu/
Technical
- Electronic Evidence is any data resulting from the output of an analogue device and/or a digital device of potential probative value that are generated by, processed by, stored on or transmitted by any electronic device.
- Digital evidence is that Electronic Evidence which is generated or converted to a numerical format.
- Private Cloud Computing
- Computing services offered through the Internet or a private internal network and only to select users instead of the general public.
- Public Cloud Computing
- Typically a private infrastructure where the services provided are rendered over a network that is open for public use.
- Hybrid Cloud Computing
- Composition of two or more clouds (private, community or public) that remain different entities but are united, offering the benefits of multiple deployment models.
- Community Cloud Computing
- Community Cloud Computing is a collaborative effort in which infrastructure is shared between several organizations from a specific community with common concerns (security, compliance, jurisdiction, etc.). This is controlled and used by a group of organizations that have shared interest.
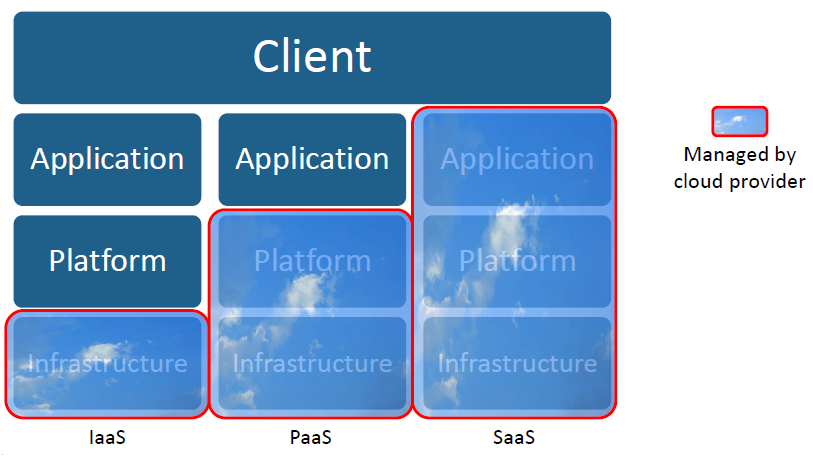
- Cloud Software as a Service - SaaS
Software distribution model where a company provides the maintenance, support and operation that the client will use during the time he hired the service. The client will use the system hosted by that company, which will maintain the client's information in their systems and provide the necessary resources to exploit that information.
The capability provided to the consumer is to use the provider’s applications running on a cloud infrastructure.
- Cloud Platform as a Service –PaaS
PaaS model is a cloud services category that provides a platform and environment that allow developers to create applications and services that work through the internet. It allows users to create software applications using tools provided by the provider, choosing the functions they wish to include to solve their needs and discarding those they do not need.
The capability provided to the consumer is to deploy onto the cloud infrastructure consumer-created or acquired applications created using programming languages and tools supported by the provider.
- Cloud Infrastructure as a Service – IaaS
Infrastructure as a Service usually works through a virtualization platform. Instead of acquiring servers, space in data center or network equipment, customers buy all these resources from an external service provider. A fundamental difference with virtual hosting is that the provisioning of these services is done completely through the web.
The capability provided to the consumer is to provision processing, storage, networks, and other fundamental computing resources where the consumer is able to deploy and run arbitrary software, which can include operating systems and applications.
- Hash value: A digital fingerprint of the data which helps to verify the integrity of a copy. It is a fixed length computational result generated from a string of data (e.g. files, directories, an entire hard disk) using a specific mathematical algorithm that creates a unique value. A minor change in the data produces a completely different hash value.
- Log: A register of events normally generated in plain text where any event can be logged. There isn’t a standard on the format, every system/application uses its own, although most of them are similar. Logs save When something happened, What happened and Who was the one that did it. It allows to know what happened in an information system. Usually laws force to keep logs for a certain amount of time.
- Cloud: datacenter infrastructure maintained by a third party that delivers on-demand virtual computing, platform and application services.
- Cloud Service Providers: Cloud service providers (CSP) are companies that offer network services, infrastructure, or business applications in the cloud. The cloud services are hosted in a data centre than can be accessed by companies or individuals using network connectivity.
- Digital forensics: The application of digital investigation and analysis techniques to perform a structured examination of a digital storage medium, while maintaining a documented chain of evidence, for the purpose of gathering information admissible in evidence in a court of law or in a disciplinary procedure.
- Chain of evidence: Refers to a detailed documentation of the status of potential digital evidence at every point of time from the moment of collection, acquisition or seizure of the evidence to the moment the evidence is presented in court.
- Digital forensic image: The forensic (bitwise) copy of original data contained on a digital storage medium, acquired during a digital forensic operation and stored in binary format with a unique hash value.
- Security copy: A copy of the digital forensic evidence and work files for the purpose of having a backup copy in case of loss, destruction or a compromised original digital forensic image.
- Digital medium/device: A medium/device containing digital data (e.g. a file server, a computer hard disk, a CD/DVD, a USB memory stick, a smartphone, a SIM card, flash memory cards, etc.).
- Digital forensic operation: A technological inspection, acquisition, and examination of digital media and/or their contents, carried out by specialists using forensic equipment and software tools. The objective is to locate, identify, collect and/or acquire and preserve data which may be relevant to an investigation, and may be used as evidence in administrative, disciplinary and judicial procedures.
- Preview: A first inspection of a digital medium using an appropriate forensic tool in order to establish whether it may contain data potentially relevant to the investigation.
- Digital forensic collection: The process of gathering the physical devices that contain potential digital evidence.
- Digital forensic acquisition: The acquisition of any data (including deleted data) stored on a digital medium through a forensic imaging process.
- Collection of electronic evidence: process of gathering items that contain potential electronic evidence in the widest sense, including search, seizure, interception and any other forms of gathering evidence by law enforcement agencies, but also capture of evidence by the private sector and any other forms of gathering potential electronic evidence.
- Preservation: Once the evidence is collected, it needs to be preserved before it can be used during the trial. Preservation is the process of maintaining and safeguarding the integrity and original condition of the potential electronic evidence, meaning that it needs to be stored in a secure way in order to safeguard against alteration, and access to the evidence needs to be restricted to persons authorised to process the evidence.






 escert.upc.edu
escert.upc.edu